The mainstream adoption of Gigabit Ethernet (1000BASE-T) required a new industry-standard cable. The cable needed to be capable of transmitting at a higher frequency of 250 MHz. As a result, cable manufacturers introduced CAT6. The CAT6 cable uses a thicker-gauge wire and has an increased shielding. Also, the wires have more twists per inch. These improvements helped to reduce signal loss and interference. The tighter specifications guaranteed that 100-meter runs using CAT6 cable is capable of 1000 Mbit/s transfer speeds. Also, CAT6 cable can reach 10-Gigabit Ethernet speeds by reducing the length to less than 50 meters. After introducing CAT6, ICC made enhancements and produced CAT6e.
Cat6 vs Cat6a
Contents
Definition
Cat6 - Category 6
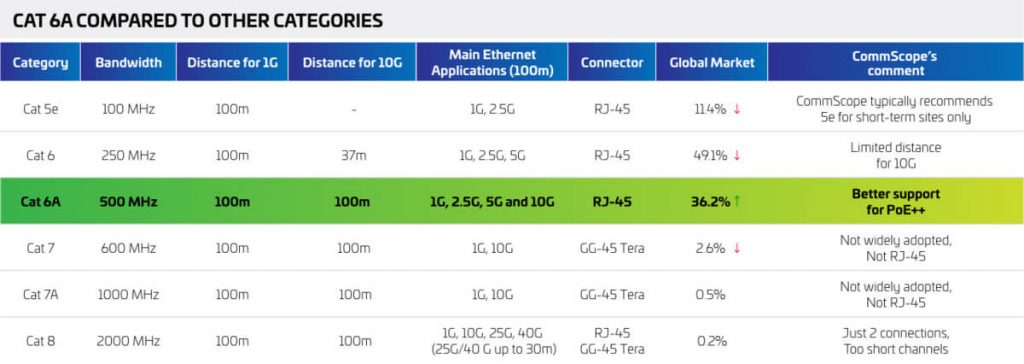
Cat 6A - Category 6A
Another version of the CAT6 standard is available; it is labeled as CAT6A and is considered an advancement of CAT6. TIA set the limit at 500MHz, which is double the CAT6 standard. The CAT6A cable can extend up to 100 meters and transfer data at a maximum data rate of 10Gbps (10GBASE-T).
How can we protect our initial investment against these changing demands?
Cat6 vs Cat6A
“How can we protect the initial investment against these changing demands?”
“Do I invest in Category 6 or Category 6A cabling?”
There is a list of considerations and variables to analyze:
- Supported applications and lifecycle
- Difference in size and space requirements
- Installation time and costs
- Material costs
- For how many years will we be using 6? And 6A?
- Total project investment
Longer life cycle is not equal to greater investment
That’s not necessarily true, if you consider that Category 6A was developed to support 10Gbps Ethernet, whereas Category 6 supports up to 1Gbps Ethernet. Therefore, the right question to ask is, “When are we implementing 10G over copper in our data center? In 3 to 5 years? What about our commercial buildings? In 5 to 7 years?”
So, if installing Cat 6 today, we might face in the future an additional investment to migrate to Cat 6A, hence, the total investment is greater than installing Cat 6A today
More occupied space is not equal to greater investment
It’s true, the outer diameter of a Category 6 cable is smaller, and so it requires smaller raceways and cable managers, and less space. For this reason, design is key, bearing in mind that larger cables will be used in the future. But don’t despair; planning for larger raceways supporting Category 6A in the design stage will save us much higher costs in the future. And after all, not all Category 6A cables are the same.
Higher Category is not equal to greater investment
Category 6A it enables higher speeds, greater bandwidth and a longer lifecycle, and so the material costs are higher than Category 6.
But a way of understanding the investment is to look at the whole picture. If we design the same raceways/ducts for Cat. 6 and 6A (foresight!) and, as we know, implementation costs are the same, the difference between Cat. 6 and Cat. 6A projects becomes smaller.
Another point to be considered is the hidden costs of some Category 6A solutions. For example, whether they support cable lengths shorter than 15 meters (less cable to be purchased); whether they support short patch cords (for example, at least 1 or 2 meters); and how many cables cable managers can accommodate (the smaller the cable managers, the lower the costs).
So what is the total cost of each project?
In order to see the “forest” (investment project) and not only the “trees” (cable vs. cable costs), the following factors should be taken into account: material costs, implementation cost, raceway/duct costs (foresight!), hidden costs (cable lengths, cord lengths, cable manager sizes) and replacement due to end of useful life (when I will have to invest again, how much dismantling the old installation and stopping operations costs).
