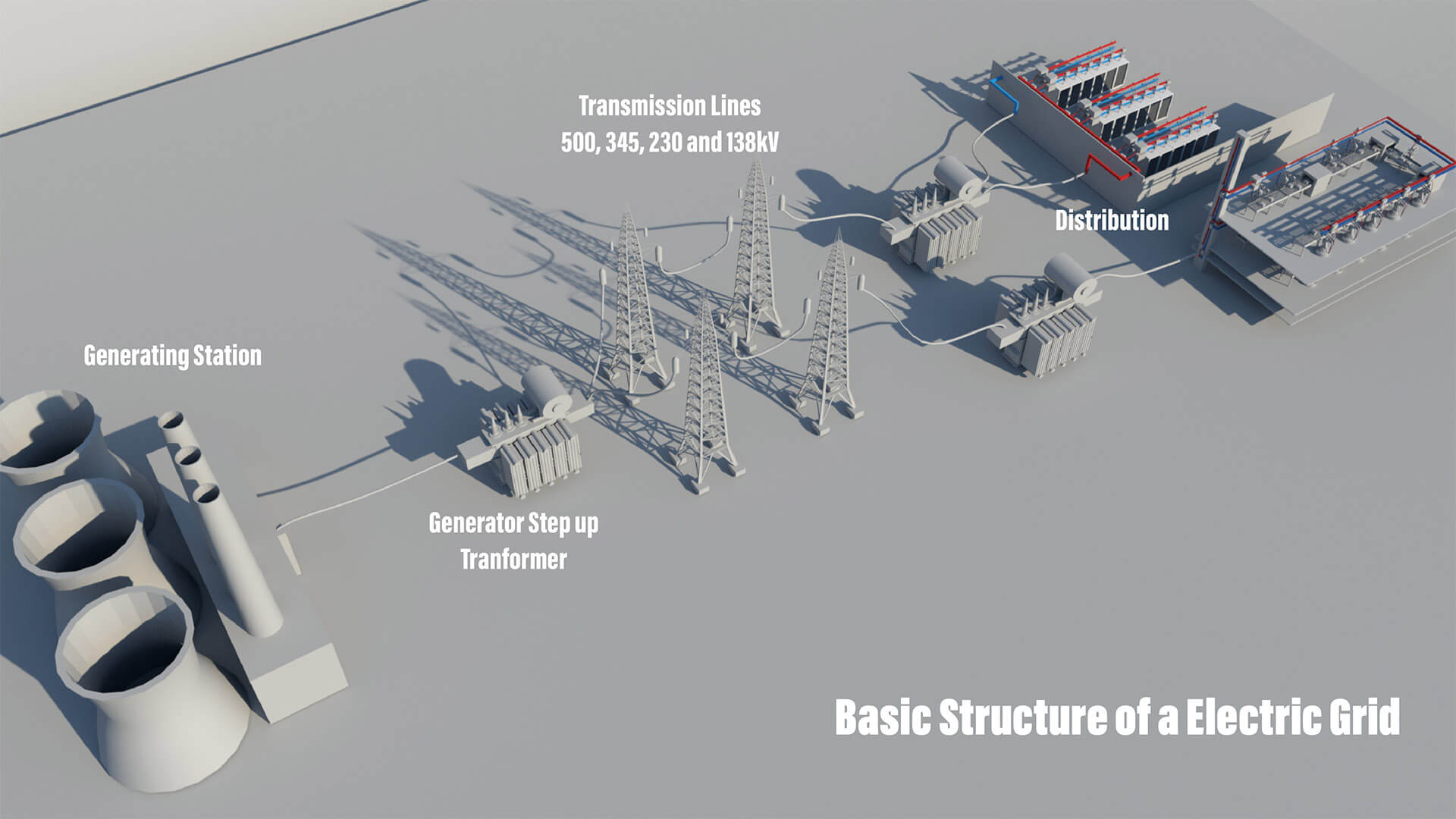
The distribution system is the part of an electric system after the transmission system that is dedicated to delivering electric energy to an end-user.
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electric power; it carries electricity from the transmission system to individual consumers. The network of lines that carries electricity from distribution substations to the homes of the consumer is called distribution lines. The distributed electricity is then used by the consumer.